
Skin Pigmentation
Skin pigmentation is the color of your skin, which is produced by melanin and is a pigment made by melanocytes—skin cells. The melanin quantity and its type determine the innate color of your skin. Moreover, melanin offers protection by protecting the skin from the damaging effects of UV radiation. Nevertheless, melanin production may fail which can in turn lead to problems related to pigmentation and result in lighter or darker spots on the skin.
Types of Pigmentation
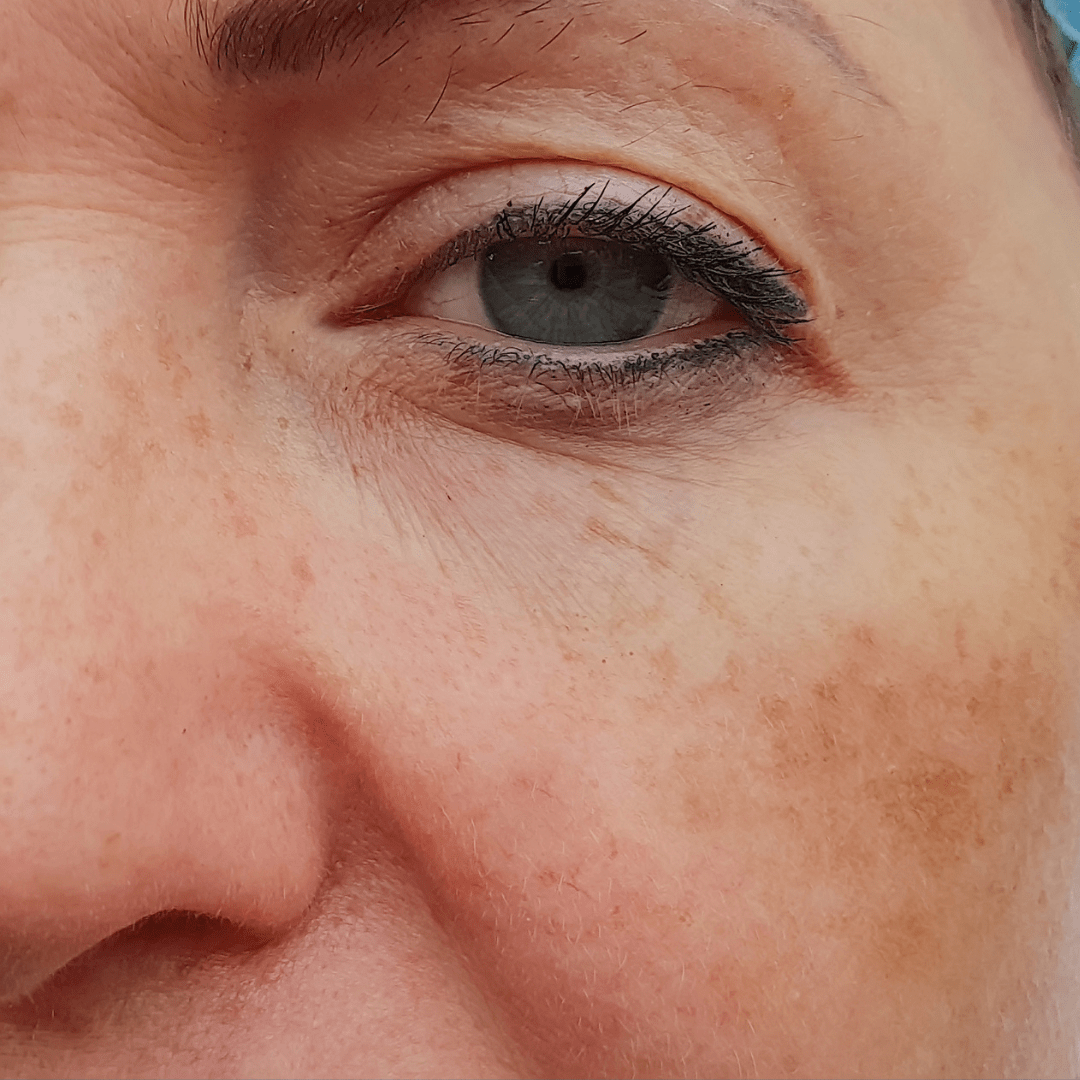

There are various pigmentation types accompanied by different causes and certain details:
- Hyperpigmentation: This is the condition in which patches of the skin are darker than the rest of your skin because of their high production of melanin.
- Hypopigmentation: This is the situation in which areas less pigmented than the normal skin color, often the result of a lessened melanin presence.
- Melasma: It is a kind of hyperpigmentation mostly caused by hormonal changes, which usually occurs on the face.
- Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation (PIH): Dark spots are the tokens of the skin injury or inflammation, such as acne.
- Freckles and Age Spots: These are small, dense areas of pigmentation from sun exposure and aging.
Treatment of Pigmentation
Topical Treatments
Hydroquinone: A skin-lightening agent that reduces hyperpigmentation by inhibiting melanin production.
Retinoids: Vitamin A derivatives like tretinoin that help in skin cell turnover and reduce dark spots.
Vitamin C: An antioxidant that brightens the skin and reduces pigmentation.
Azelaic Acid: Helps to treat pigmentation, especially in conditions like melasma and post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation.
Kojic Acid: Derived from fungi, it helps lighten skin and reduce dark spots.
Niacinamide: A form of Vitamin B3 that can reduce the appearance of dark spots and improve skin tone.
2. Chemical Peels
Glycolic Acid Peels: Exfoliates the skin, helping to remove the outer layer of dead skin cells and lighten dark spots.
Salicylic Acid Peels: Good for treating pigmentation related to acne scars.
TCA Peels: Stronger peels that target deeper pigmentation.
3. Laser Treatments
Fractional Lasers: Targets deeper layers of the skin to break down pigmentation and stimulate collagen production.
Q-switched NdLaser: Specifically targets melanin to reduce dark spots and pigmentation.
4. Microdermabrasion
A procedure that exfoliates the skin using tiny crystals, helping to remove superficial pigmentation.
5. Microneedling
Involves using fine needles to create micro-injuries in the skin, promoting healing and reducing pigmentation over time.
6. Sun Protection
Sunscreen: Daily use of broad-spectrum sunscreen (SPF 30 or higher) is crucial to prevent further pigmentation and protect treated areas.
Physical Barriers: Wearing hats, sunglasses, and protective clothing can also help prevent sun-induced pigmentation.
7. Oral Treatments
Tranexamic Acid: Sometimes prescribed orally for stubborn cases of melasma.
Antioxidants: Oral supplements like Vitamin C, E, and glutathione can support skin health and reduce pigmentation.
8. Home Remedies
Aloe Vera: Known for its skin-soothing properties, it can help lighten pigmentation when used regularly.
Lemon Juice: Contains natural bleaching properties, but should be used with caution due to potential irritation.
Turmeric: An anti-inflammatory that can help in reducing dark spots when used in masks.
9. Lifestyle Modifications
Healthy Diet: A diet rich in antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals supports skin health.
Avoiding Triggers: Identifying and avoiding triggers such as sun exposure or certain medications can prevent pigmentation from worsening.
10. Consultation with a Dermatologist
For persistent or severe pigmentation issues, consulting a dermatologist is crucial. They can provide personalized treatment plans and monitor your progress.
